
Refractive Error
For humans to appreciate clear vision, light rays must be bent or refracted by the clear window at the front of the eye termed the ‘Cornea’ and the lens so that they can focus on the retina (which forms the inner coat of back of the eye). The retina receives the image formed by these light rays and sends it to the brain through the optic nerve.
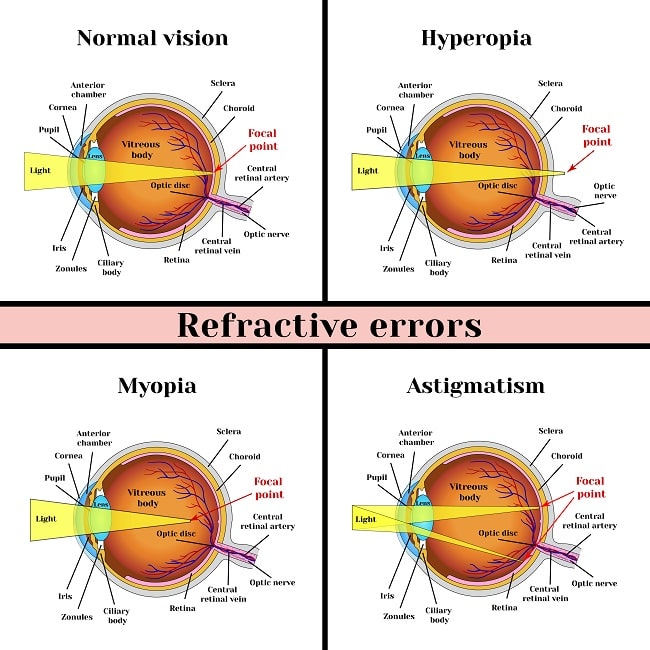
A refractive error means that light rays are not focused to a fine point on the retina resulting in blurred vision.
What is myopia?
In Myopia (Short sightedness), the eye is longer than normal or the cornea is too steep, so that light rays focus in front of the retina. Near objects are clear but distant objects appear blurred.
What is hyperopia / hypermetropia?
In Hypermetropia (Long sightedness), the eye is shorter than normal or the cornea is too flat, so that light rays focus behind the retina. Light rays from close objects such as pages of a book cannot focus clearly on the retina.
What is astigmatism?
In Astigmatism (Distorted vision), the cornea is more curved in one direction than in the other. This results in vision being blurred for both near and distant objects.
What is presbyopia?
When we are young, the lens in the eye can change its shape allowing us to focus on near objects. After the age of 40, the lens becomes noticeably more rigid and hence reading at close range becomes increasingly difficult. This condition is called presbyopia and is a normal part of ageing.

